Pomegranate peel has protective effects against enteropathogenic bacteria
08/31/2021 // Ralph Flores // Views
Tags: alternative medicine, E. coli, food as medicine, food cures, food science, functional food, goodfood, goodhealth, goodscience, infection, infections, natural antibiotics, natural cures, natural medicine, phenols, phytonutrients, polyphenols, pomegranate, pomegranate peel, remedies, research
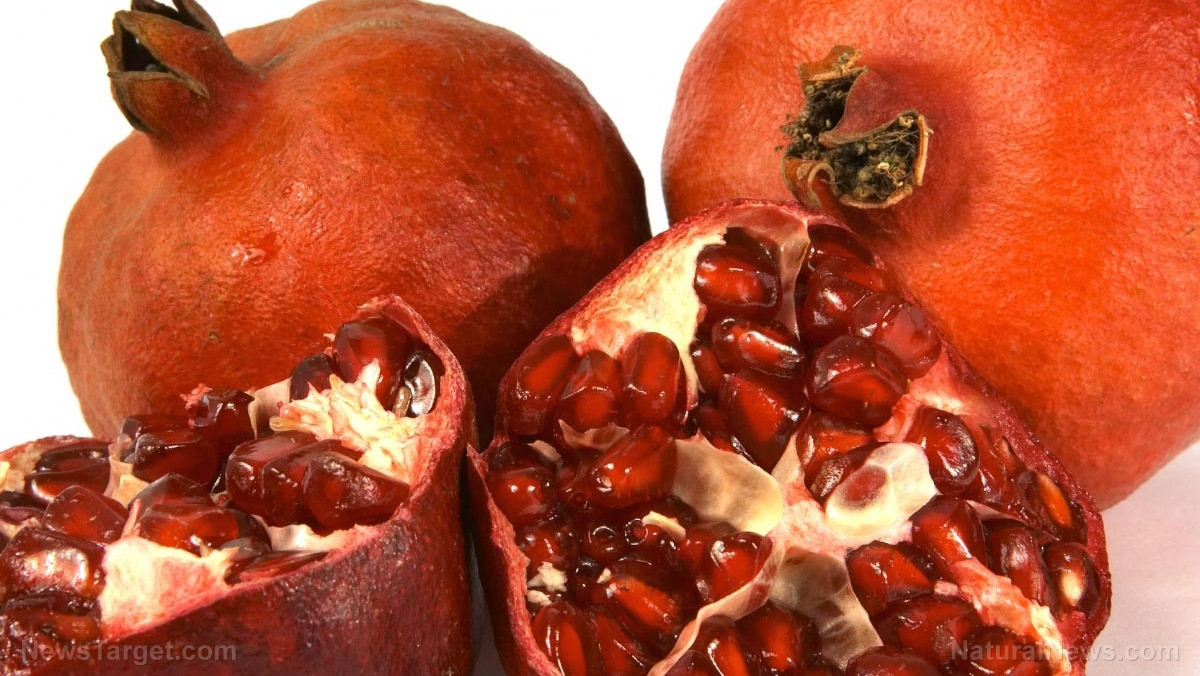

- Pomegranate fruit peel is considered an agricultural waste product. However, it is a rich source of polyphenols like punicalins, punicalagins and ellagic acids.
- Earlier studies have shown that products derived from pomegranates have health benefits, including antibacterial activity, in vitro.
- There is limited evidence, however, of their antibacterial activity in vivo.
- For this study, researchers sought to determine the antibacterial properties of pomegranate peel extract in vivo. In particular, they focused on the punicalin, punicalagin and ellagic acid present in the peel extract.
- The researchers infected C3H/He mice with the bacterial pathogen Citrobacter rodentium, a bacterium that mimics the enteropathogenic bacterium, Escherichia coli. Prior to infection, the mice were orally treated with water or pomegranate peel extract.
- Twelve days after infection, the researchers examined C. rodentium colonization of the colon and spleen, as well as changes in tissue and gene expression. Fecal excretions were also analyzed for C. rodentium.
- The results revealed that the pomegranate peel extract reduced weight loss and mortality induced by C. rodentium infection.
- The extract also reduced C. rodentium colonization of the spleen.
- Additionally, pomegranate peel extract decreased the extent of damage in the colon caused by C. rodentium infection.
In sum, pomegranate fruit peel extract contains bioactive compounds that can help reduce the severity of C. rodentium infection in vivo.
Learn more about other natural food-based treatments at FoodScience.news.
Journal Reference:
Smith AD, George NS, Cheung L, Bhagavathy GV, Luthria DL, John KM, Bhagwat AA. POMEGRANATE PEEL EXTRACT REDUCED COLONIC DAMAGE AND BACTERIAL TRANSLOCATION IN A MOUSE MODEL OF INFECTIOUS COLITIS INDUCED BY CITROBACTER RODENTIUM. Nutrition Research. 2019 Nov 16; 73: 27–37. DOI: 10.1016/j.nutres.2019.11.001
Related Topics
alternative medicine E. coli food as medicine food cures food science functional food goodfood goodhealth goodscience infection infections natural antibiotics natural cures natural medicine phenols phytonutrients polyphenols pomegranate pomegranate peel remedies researchLatest News
Related News
11/21/2023 / By Arsenio Toledo
11/21/2023 / By Evangelyn Rodriguez
11/21/2023 / By Zoey Sky
11/20/2023 / By Arsenio Toledo
11/17/2023 / By Zoey Sky
11/15/2023 / By Kevin Hughes
Take Action:
Support Natural News by linking to this article from your website.
Permalink to this article:
Copy
Embed article link:
Copy
Reprinting this article:
Non-commercial use is permitted with credit to NaturalNews.com (including a clickable link).
Please contact us for more information.
Please contact us for more information.