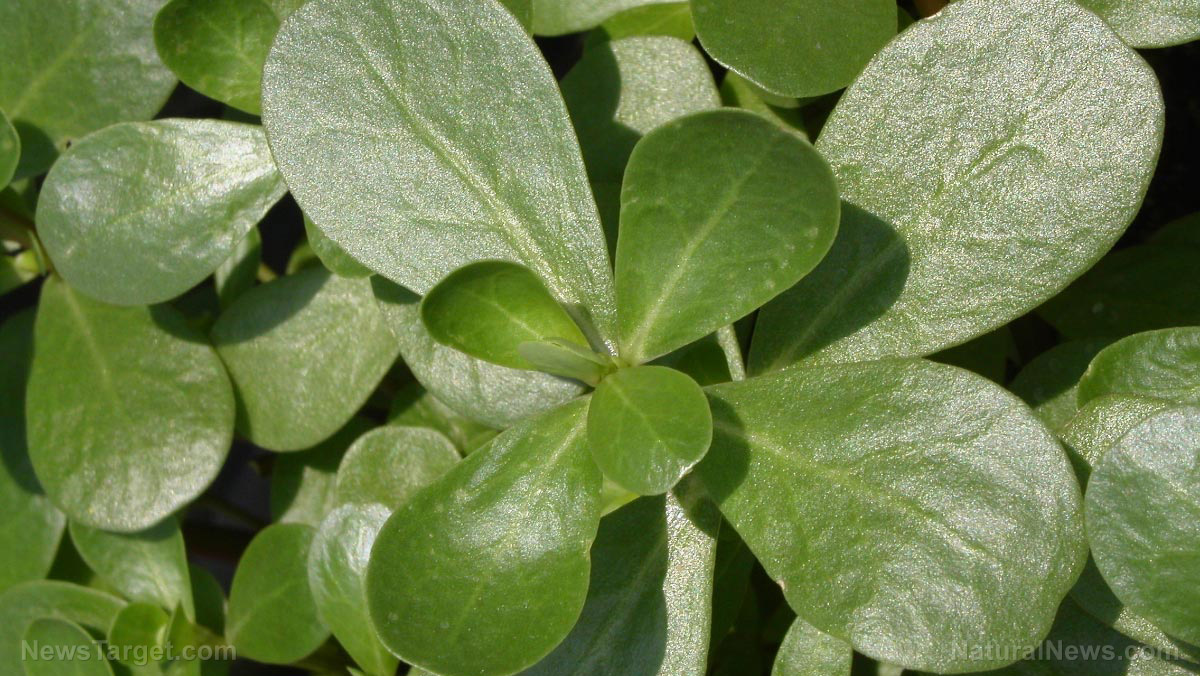
A look into the anti-carcinogenic effects of Portulaca oleracea polysaccharides
06/08/2020 // Evangelyn Rodriguez // Views
Tags: alternative medicine, anti-cancer, cancer cures, cancer solutions, disease treatments, food cures, food is medicine, functional food, goodcancer, goodfood, goodhealth, goodmedicine, goodscience, natural cures, natural medicine, prevention, research, superfoods, veggie, women's health

- Cervical cancer is the second most prevalent cancer in the world.
- Studies have found that POL-P3b can enhance immunity and exerts anti-cancer effects when taken orally.
- To further investigate this, the researchers isolated intestinal dendritic cells (DC), which play a key role in regulating intestinal immune homeostasis, from U14-bearing mice treated with 50?mg/kg, 100?mg/kg and 200?mg/kg POL-P3b.
- They used MTT assay and staining techniques to evaluate the effects of POL-P3b on DC proliferation and apoptosis.
- They also used flow cytometry to analyze mitochondrial calcium uptake and Western blotting to determine the mechanisms underlying POl-P3b-induced protection of intestinal DC from cervical cancer-induced apoptosis.
- The researchers found that a large number of intestinal DC were undergoing apoptosis in U14-bearing mice.
- POL-P3b treatment at different doses for 12 days significantly improved intestinal DC survival.
- It also protected intestinal DC against tumor-induced apoptosis by activating the TLR4/PI3K/AKT-NF-kB signaling pathway, which increased Bcl-2 and mitochondrial calcium levels, prevented the release of cytochome c from mitochondria and reduced the expression of caspase 3.
Based on these findings, the researchers concluded that oral POL-P3b exerts its anti-cancer effects against cervical cancer by inhibiting apoptosis.
Read the full study at this link.
Journal Reference:
Zhao R, Shao X, Jia G, Huang Y, Liu Z, Song B, Hou J. ANTI-CERVICAL CARCINOMA EFFECT OF PORTULACA OLERACEA L. POLYSACCHARIDES BY ORAL ADMINISTRATION ON INTESTINAL DENDRITIC CELLS. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2019;19(1). DOI: 10.1186/s12906-019-2582-9
Related Topics
alternative medicine anti-cancer cancer cures cancer solutions disease treatments food cures food is medicine functional food goodcancer goodfood goodhealth goodmedicine goodscience natural cures natural medicine prevention research superfoods veggie women's healthLatest News
Related News
07/10/2023 / By Zoey Sky
07/05/2023 / By Ethan Huff
07/05/2023 / By Kevin Hughes
07/04/2023 / By Olivia Cook
07/04/2023 / By Zoey Sky
Take Action:
Support Natural News by linking to this article from your website.
Permalink to this article:
Copy
Embed article link:
Copy
Reprinting this article:
Non-commercial use is permitted with credit to NaturalNews.com (including a clickable link).
Please contact us for more information.
Please contact us for more information.