Exploring the anti-carcinogenic potential and biosafety of Indian propolis
04/09/2020 // Evangelyn Rodriguez // Views
Tags: alternative medicine, anti-cancer, bee products, cancer cures, cancer solutions, cancer treatments, disease treatments, goodcancer, goodhealth, goodmedicine, goodscience, Indian propolis, natural cures, natural medicine, phytonutrients, prevent cancer, research
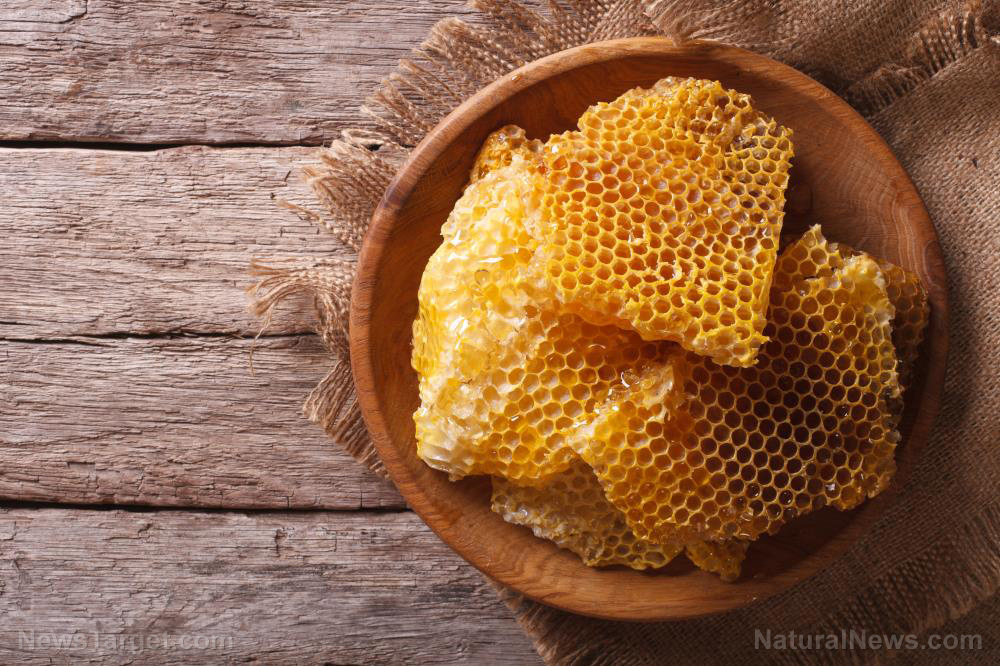

- Propolis from apiculture has a wide range of medicinal properties, thanks to its abundance in phytonutrients, such as polyphenols, flavonoids and the anti-cancer agent, caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE).
- For their analysis, the researchers extracted, optimized and standardized IP using a newly developed and validated liquid chromatography method that simultaneously estimates caffeic acid, apigenin, quercetin and CAPE content.
- Then, they screened the standardized ethanolic extract of IP (EEIP) for in vitro cytotoxicity, anti-carcinogenic effect (against Dalton’s Lymphoma ascites (DLA) cells), hemolytic effect and pesticidal potential.
- The researchers found that EEIP contains more flavonoids, polyphenolic compounds and all the selected markers except for caffeic acid, than IP extracts obtained using other solvents.
- EEIP also showed better anti-cancer activities than CAPE on MCF-7 and HT-29 cells in vitro.
- In vivo, EEIP had better anti-carcinogenic effects against DLA than 5-fluorouracil. It also proved to be non-hemolytic.
Based on these findings, the researchers concluded that the standardized EEIP is a safe anti-carcinogenic agent that can be further developed into a natural anti-cancer medicine.
Read the full study at this link.
Journal Reference:
Kapare H, Lohidasan S, Sinnathambi A, Mahadik K. STANDARDIZATION, ANTI-CARCINOGENIC POTENTIAL AND BIOSAFETY OF INDIAN PROPOLIS. Journal of Ayurveda and Integrative Medicine. 2019;10(2):81–87. DOI: 10.1016/j.jaim.2017.06.003
Related Topics
alternative medicine anti-cancer bee products cancer cures cancer solutions cancer treatments disease treatments goodcancer goodhealth goodmedicine goodscience Indian propolis natural cures natural medicine phytonutrients prevent cancer researchLatest News
Related News
07/10/2023 / By Zoey Sky
07/05/2023 / By Ethan Huff
07/05/2023 / By Kevin Hughes
07/04/2023 / By Olivia Cook
07/04/2023 / By Zoey Sky
Take Action:
Support Natural News by linking to this article from your website.
Permalink to this article:
Copy
Embed article link:
Copy
Reprinting this article:
Non-commercial use is permitted with credit to NaturalNews.com (including a clickable link).
Please contact us for more information.
Please contact us for more information.