More should be done to fight air pollution, experts say
Findings from a benchmark study suggest the growing threat is worsening in its global epicenter, South Asia.
However, the level of funding set aside to address air pollution is only a small fragment of the amount reserved for research on the prevention of infectious diseases, said researchers from the Energy Policy Institute at the University of Chicago (EPIC).
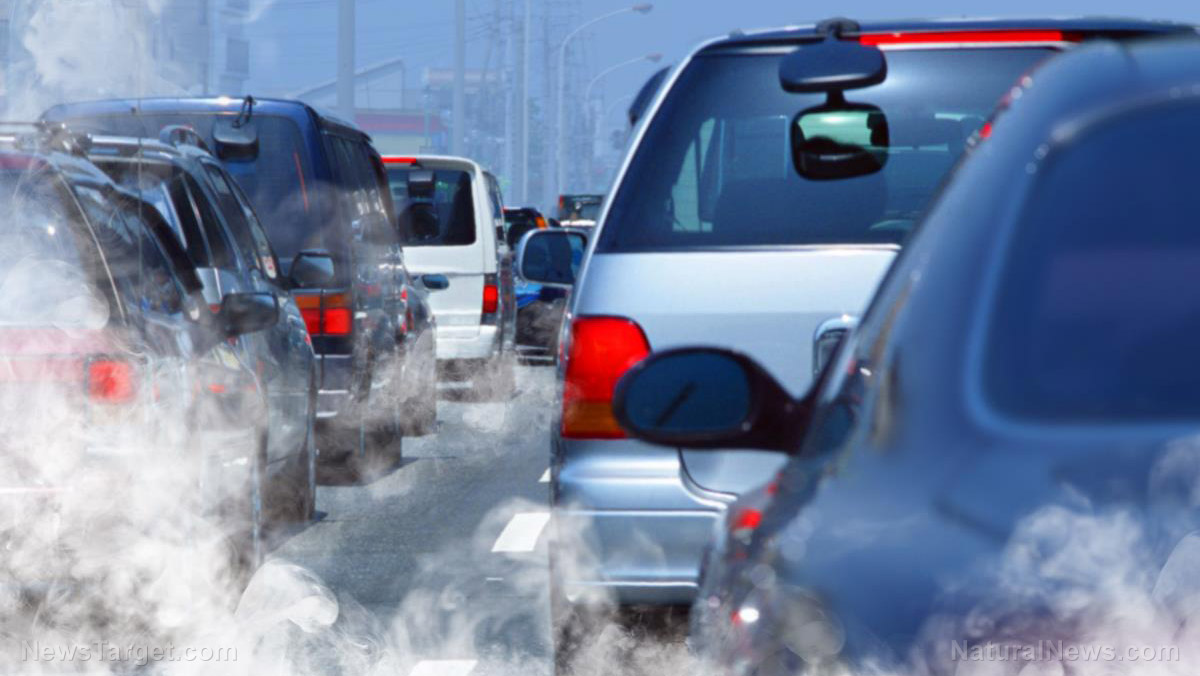
EPIC's Air Quality Life Index (AQLI) report revealed that fine particulate air pollution, which is produced by vehicle and industrial emissions, wildfires and other sources, is still the "greatest external threat to public health."
The data, which has a 2021 cutoff, suggests that if measures are enforced to permanently reduce these pollutants to meet the guideline limit set by the World Health Organization (WHO), the average person would add 2.3 years to his life expectancy.
Fine particulate matter is dangerous and research has found that it can cause health issues like cancer, heart disease, lung disease and stroke.
On the other hand, tobacco use reduces global life expectancy by 2.2 years, while child and maternal malnutrition reduces life expectancy 1.6 years. (Related: New York City’s air quality reaches “hazardous” level – one of the worst recorded in decades.)
Both Asia and Africa bear the greatest burden yet have some of the weakest infrastructure to provide citizens with timely, accurate data. These areas receive only a small fraction of a limited global philanthropic movement. The entire continent of Africa receives less than $300,000 to address air pollution.
Christa Hasenkopf, director of air quality programs at EPIC, explained that there is a significant disconnect between where air pollution is the worst and where people are collectively and globally deploying resources to fix the problem.
For example, there is an international financing partnership called the Global Fund that disburses $4 billion annually for research on HIV/AIDS, malaria and tuberculosis, but there is no equivalent for air pollution.
According to the AQLI report, "air pollution shaves off more years from the average person's life in the DRC (Democratic Republic of Congo) and Cameroon than HIV/AIDS, malaria, and other health threats."
South Asia the "worst impacted region"
Globally, South Asia is the region that is worst impacted by air pollution.
Meanwhile, countries like Bangladesh, India, Nepal and Pakistan are in order the top four most polluted countries in terms of annualized, population-weighted averages of fine particulate matter, which are detected by satellites and defined as particles with a diameter of 2.5 microns or less (PM2.5).
Air pollution concentrations are fed into the AQLI metric which calculates their impact on life expectancy. The process is based on peer-reviewed methods.
Residents of Bangladesh, where average PM2.5 levels are 74 micrograms per cubic meter, would gain at least 6.8 years of life if PM2.5 levels were brought to WHO guidelines of 5 micrograms per cubic meter.
Delhi, India's capital, is the most polluted megacity in the world. Delhi has an annual average particulate pollution of 126.5 micrograms per cubic meter.
Hasenkopf said that China has made significant progress in how it is addressing air pollution, which began in 2014. China's air pollution dropped by as much as 42.3 percent between 2013 and 2021.
If the country can sustain these improvements, the average Chinese citizen will be able to live 2.2 years longer.
America's ongoing battle with air pollution
In the U.S., legislative actions like the Clean Air Act has helped reduce pollution by as much as 64.9 percent since 1970, helping Americans gain 1.4 years of life expectancy.
However, the growing threat of wildfires are causing pollution spikes from the western U.S., all the way to Latin America and Southeast Asia.
In 2021, California's historic wildfire season included Plumas County receiving an average concentration of fine particulate matter more than five times over WHO guidelines.
North America's story of air pollution improvements in recent decades is similar to Europe, but there are still noticeable differences between western and eastern Europe. To date, Bosnia is the continent's most polluted country.
Tips for preventing air pollution at home
Even if your home is always clean and tidy, it can also be a source of air pollution.
Follow these tips to prevent air pollution at home:
- Avoid smoking indoors or quit smoking completely.
- Always use craft supplies in well-ventilated rooms.
- Keep a gas stove in a well-ventilated area.
- Organize all items and minimize clutter.
- Avoid using carpeting if possible.
- Use a dehumidifier or an air conditioner to reduce moisture.
- Minimize air freshener use or avoid using it completely.
- Always keep trash covered to avoid attracting pests.
- Remove your shoes before entering your home.
- Install carbon monoxide detectors.
- Have car emissions tested regularly.
- Test your home for radon.
- Fix all water leaks.
- Dust all surfaces and vacuum your house frequently.
- Wash bedding weekly in hot water.
- Check that all exhaust fans are functioning in your bathrooms and the kitchen.
Keep your home clean and quit smoking to reduce exposure to air pollution.
Visit Pollution.news for more information on the adverse effects of air pollution on human health and the environment.
Watch the video below to learn more about toxic air poisoning cities in America.
This video is from the KryptoKing187 on Brighteon.com.
More related stories:
Canadian wildfire smoke continues to affect air quality in US cities.
Report: People across America are routinely exposed to vinyl chloride pollution.
Ways to keep indoor air clean when there’s wildfire smoke in your area.
Sources include:
Please contact us for more information.