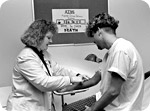
Scientists Develop Blood Test to Detect Alzheimer's Disease
Sunday, November 09, 2008 by: Margaret Priddy
Tags: Alzheimer's, health news, Natural News
- Sea cucumber extract kills 95 percent of breast cancer cells and shrinks lung tumors
- The REAL FAKE NEWS exposed: '97% of scientists agree on climate change' is an engineered hoax... here's what the media never told you
- Polish study says vaccines have no historical benefits, continue to cause neurological damage
- The truth about tanning beds: They boost vitamin D production
- Hurricane warnings wildly exaggerated by NOAA to terrorize Americans about climate change
- Six little-known natural remedies for tinnitus
- The many health benefits of Moringa oleifera
- Five cancer-fighting recipes that also help you beat the summer heat
- How laetrile or B17 from apricot seeds kills only cancer cells
- Urgent: What to Do If You Cannot Avoid Flu Shots or are Exposed to Virus Shedding
- The Gerson Therapy: Big Pharma and the AMA Suppress Another Holistic Cancer Cure
- Poultry industry, like the beef industry, is steeped in evil practices
- How to heal cavities naturally
- Discover a common yard weed that's proven to kill cancer cells
- Aajonus Vonderplanitz PhD, key informant in prosecution of Sharon Palmer and James Stewart, found to have faked academic credentials
- Clear heart blockages with this powerful lemon and garlic mixture
- Use natural remedies for a hiatal hernia
- Beat cancer with 35% hydrogen peroxide
- The REAL FAKE NEWS exposed: '97% of scientists agree on climate change' is an engineered hoax... here's what the media never told you
- Ginger over chemo: This powerful root can eliminate 10,000x the number of cancer cells
- Sea cucumber extract kills 95 percent of breast cancer cells and shrinks lung tumors
- Untested vaccines causing new wave of polio-like paralysis across India
- Study shows nutritional supplements can cut hospital readmission rates
- Apricot Seeds Kill Cancer Cells without Side Effects
- How to heal cavities naturally
- The many health benefits of Moringa oleifera
- Grow your own ginger for free: Natural medicine that's delicious too!
- Dr. David Gorski named in medical conspiracy allegations complaint filed with Karmanos Cancer Center and Michigan Attorney General
- Genital Herpes May be Reversed with Natural Medicine
- The truth about tanning beds: They boost vitamin D production
- Four proven natural remedies for chronic inflammation
- Beat cancer with 35% hydrogen peroxide
- Avoid vaccines and use these top four natural remedies for flu prevention instead
- Mainstream media finally admits U.S. honey is contaminated with glyphosate weed killer (Roundup)
- Discover a common yard weed that's proven to kill cancer cells
- Bill Gates says vaccines can help reduce world population
- Six little-known natural remedies for tinnitus
- High-dose vitamin C injections shown to annihilate cancer
- Supplements to detox the body from vaccinations
- The REAL FAKE NEWS exposed: '97% of scientists agree on climate change' is an engineered hoax... here's what the media never told you
- Four proven natural remedies for chronic inflammation
- Beat cancer with 35% hydrogen peroxide
- Olive oil antioxidant naturally kills all cancer cells tested within an hour
- Apricot Seeds Kill Cancer Cells without Side Effects
- Foods that detox heavy metals - with tonic recipe
- Cannabis kicks Lyme disease to the curb
- Top 10 inexpensive food items that can PREVENT nearly every disease and disorder known to mankind
- Four bitter herbs heal the liver, gall bladder, and other ailments
- The aloe vera miracle: A natural medicine for cancer, cholesterol, diabetes, inflammation, IBS, and other health conditions
- Clear heart blockages with this powerful lemon and garlic mixture
- Curcumin causes colon cancer cells to self-destruct
- Foods, herbs, and supplements that kill cancer - safer and more effective than drugs
- The best and worst forms of magnesium to take as a supplement
- Frankincense oil kills cancer cells while boosting the immune system, studies show
- EPA advisor admits the agency is funneling billions to climate groups ahead of Trump’s return to White House
- Newly released JFK files reveal Pentagon's role in creating Lyme disease and covid in the same lab
- Eleven days before Iran bombed Tel Aviv, my microscope revealed haunting images of EXACTLY what would happen
- Morphic resonance “remote viewing” reveals iconic Middle East images of stealth bombers, a falcon and a one-horned ram
- Mike Adams releases country western hit single: Goin’ Back in Time is Comin’ Home
- DECENTRALIZED SPIRITUALITY and the true teachings of Christ: Overcoming the censorship, threats and lies of organized religion to truly know God and the Universal Christ
- Global leaders unite to clamp down on “misinformation” with UN-backed Cascais Declaration
- HEALTH SECRETS: How to Instantly Block MSG Toxicity Using Natural Substances (and the secret of Methylene Blue)
- I Want My Bailout Money – new song released by Mike Adams
- The Health Ranger releases “Vaccine Zombie” song and music video, using AI-animated zombies for the music video
- BOMBSHELL: Internal Pfizer documents exposed and reveal at least 16 PERCENT of their mRNA vaccine "adverse events" are REPRODUCTIVE DISORDERS
- BOMBSHELL: DNA testing kits are a SCAM to develop ethnic-specific bioweapons
- BOMBSHELL: Covid-19 mRNA nanoparticles EMIT LIGHT SIGNALS that communicate MAC addresses used for self-assembly inside the blood vessels
- Amazing microscopy photos reveal how freezing crystals attempt to mimic electronic structures they are touching
- RFK Jr. clears key hurdle: Sen. Susan Collins backs controversial HHS nominee, signaling a new era for health policy
- The Coming Gold Revaluation: Strategic Financial Realignment in an Era of Dollar Collapse
- Two containers with completed ballots fall out of truck in Florida
- The AI Data Center Wars Have Begun… Farms, Water and Electricity is Stripped from Humans to Power the Machines
The brain sends signals to the body's immune system. These signals pick up changes in the blood proteins in the brain. Scientists can then "eavesdrop" on how the cells communicate with each other. Certain changes in blood proteins produce a pattern that's characteristic to Alzheimer's.
It is difficult to diagnose Alzheimer's since there is no definitive test for the disease. Diagnosis is usually made by excluding other possible causes of memory loss such as brain tumors, head injuries, stroke, alcoholism, drug abuse, dehydration, and vitamin B12 and folic acid deficiencies. Even when a diagnosis of Alzheimer's is made, the only way to be sure of the diagnosis is upon autopsy, where under microscopic examination, the brain reveals twisted fragments of protein. This plaque normally occurs with age but is more pronounced in Alzheimer's.
According to the Alzheimer's Association, more that 5 million Americans are afflicted with the disease. The disease presents a picture of progressive physical and mental decline to the point of total disability. There is memory loss, confusion, depression, paranoia and impaired decision-making ability. Sufferers misplace items, experience hallucinations and delusions, get lost and are eventually unable to recognize family members. Loss of bowel and bladder occur as well as an inability to communicate. Individuals usually die in less than 15 years.
A commercial blood test for Alzheimer's will be developed for use in research labs and will eventually be used as a diagnostic test upon approval. But scientists state that it may be a few years before the test is approved for use by doctors. The test would be offered to those whose close relatives had the disease and who may be suffering memory loss themselves.
Many individuals say they would not want to know if they would develop the disease. Others state that they would want to know so they could get their affairs in order: affairs such as writing a will, modifying their home environment, and enlisting support from friends and family. Still others fear that insurance companies would raise rates for those at risk or deny coverage altogether.
An early diagnosis might give patients a chance to make changes to their diet and exercise more in an effort of slowing or staving off chances of getting the disease.
Heredity only plays a part in an individual getting Alzheimer's. Heredity does not result in Alzheimer's by itself. Environmental factors likely contribute to the overall picture. Research has been done into environmental factors such as free radicals. These are unbalanced molecules that cause damage to cells. Proper nutrition and herbal treatments prevent and fight damage from free radicals.
It is prudent to avoid substances such as aluminum (found in many products including antiperspirants and cookware) and mercury since they can be taken into the body and reside in tissues. These toxins may contribute to the development of Alzheimer's.
Some researchers believe that cortisol, a stress hormone, is a causative factor in Alzheimer's disease when elevated over a prolonged period of time. Also, homocysteine is a by-product of protein metabolism and when elevated, may contribute to Alzheimer's.
A German government study used ginkgo biloba daily for 3 months on patients with early Alzheimer's and discovered that the patients had improved memory, attention and mood.
Other natural therapies some doctors are using are as follows:
* Folate, or vitamin B9, is important to the nervous system. Folate, along with other B vitamins, help eliminate homocysteine from the blood.
* Vitamin E is also an antioxidant and a scavenger of free radicals. A 2-year study showed that Alzheimer's patients who took vitamin E supplements had improved symptoms as compared to those who took a placebo. Vitamin E is fat soluble and readily enters the brain where it is thought to slow cell damage.
* Ashwagandha (Withania somniferum) is used as a brain tonic and reduces stress hormone levels. Take according to recommendation on product label.
* DHEA is a hormone used to help cognitive function. If levels are low in the body, the doctor may start a patient on 15 mg.
* A good antioxidant will help fight free radicals.
* Chlorella aids in the detoxification process of heavy metals.
About the author
Margaret Priddy has been a registered nurse for over 25 years and has assisted in the treatment of many individuals suffering from illnesses. She has now shifted her focus to disease prevention.Alzheimer's at FETCH.news
Get independent news alerts on natural cures, food lab tests, cannabis medicine, science, robotics, drones, privacy and more.
Take Action: Support Natural News by linking to this article from your website
Permalink to this article:
Embed article link: (copy HTML code below):
Reprinting this article:
Non-commercial use OK, cite NaturalNews.com with clickable link.
Follow Natural News on Facebook, Twitter, Google Plus, and Pinterest
Science News & Studies
Medicine News and Information
Food News & Studies
Health News & Studies
Herbs News & Information
Pollution News & Studies
Cancer News & Studies
Climate News & Studies
Survival News & Information
Gear News & Information
News covering technology, stocks, hackers, and more


"Big Tech and mainstream media are constantly trying to silence the independent voices that dare to bring you the truth about toxic food ingredients, dangerous medications and the failed, fraudulent science of the profit-driven medical establishment.
Email is one of the best ways to make sure you stay informed, without the censorship of the tech giants (Google, Apple, Facebook, Twitter, YouTube, etc.). Stay informed and you'll even likely learn information that may help save your own life."
–The Health Ranger, Mike Adams























