Medical robot kills Ebola with UV light
Friday, October 10, 2014 by: David Gutierrez, staff writer
Tags: Ebola, UV light, medical robot
- The REAL FAKE NEWS exposed: '97% of scientists agree on climate change' is an engineered hoax... here's what the media never told you
- The missing link - How to beat cancer with garlic
- Mainstream media finally admits U.S. honey is contaminated with glyphosate weed killer (Roundup)
- Bullet proof immune system - how to not get a cold ever
- The stock market is 70% overvalued ... crash now inevitable
- Six little-known natural remedies for tinnitus
- BPA makes breast cancer tumors resistant to chemotherapy
- Serrapeptase is an Inexepensive Natural Miracle Medication
- Ginger over chemo: This powerful root can eliminate 10,000x the number of cancer cells
- India's organic rice success story proves that GMOs are unnecessary
- Marine Phytoplankton is Next Revolutionary Superfood for Disease Prevention and Extraordinary Health
- Many U.S. police use cell phones to track suspects instead of getting legal warrants
- Big Pharma's medical research papers are total bunk... hundreds were fraudulently ghostwritten by a P.R. firm called 'DesignWrite'
- Apricot Seeds Kill Cancer Cells without Side Effects
- INVESTIGATION: Three days before Dr. Bradstreet was found dead in a river, U.S. govt. agents raided his research facility to seize a breakthrough cancer treatment called GcMAF
- Fox network launching new TV series that glorifies Lucifer; marketed with pro-Satan tweets
- Indian black salve: The magical cancer cure
- Cleanest sources for chlorella revealed: Natural News publishes metals contamination test results for world's most famous superfood
- The REAL FAKE NEWS exposed: '97% of scientists agree on climate change' is an engineered hoax... here's what the media never told you
- Bullet proof immune system - how to not get a cold ever
- The missing link - How to beat cancer with garlic
- The benefits of growing your own garlic
- HPV and Hepatitis B vaccines do not prevent cervical cancer and liver disease
- How to reduce your toxic heavy metal load simply and cheaply
- Early warning signs of cancer that cannot be ignored
- Garlic's healing properties are so intense that it is 100 times more effective than antibiotic treatments
- Radiation, chemtrails, fertilizers: Humans are crossing "planetary boundaries" and killing Earth, study says
- The best and worst forms of magnesium to take as a supplement
- Xylitol - Is It Safe or Effective?
- Vitamin C shown to annihilate cancer
- Chinese government suspends Hepatitis B vaccines after 8 horrific infant deaths
- Natural News launches 'miracle' Ozone Dentistry product for gum care: O3 Essentials OraJuvenate
- Serrapeptase is an Inexepensive Natural Miracle Medication
- Forget Filling Cavities: Regrow Your Teeth Instead
- Three artificial chemicals that are making us fat
- Red Cabbage Found to Contain 36 Anti-Cancer Anthocyanins
- The REAL FAKE NEWS exposed: '97% of scientists agree on climate change' is an engineered hoax... here's what the media never told you
- Six little-known natural remedies for tinnitus
- High-dose vitamin C injections shown to annihilate cancer
- Four proven natural remedies for chronic inflammation
- Beat cancer with 35% hydrogen peroxide
- Oregon man convicted of collecting rainwater on his own property surrenders and begins serving 30-day jail sentence
- Dandelion root extract found to kill leukemia cells, prostate cancer cells and chemo-resistant melanoma
- Untested vaccines causing new wave of polio-like paralysis across India
- Apricot Seeds Kill Cancer Cells without Side Effects
- The best and worst forms of magnesium to take as a supplement
- Forget Filling Cavities: Regrow Your Teeth Instead
- Dandelion root far more effective in fighting cancer cells than chemotherapy
- Red Cabbage Found to Contain 36 Anti-Cancer Anthocyanins
- Bullet proof immune system - how to not get a cold ever
- Sea cucumber extract kills 95 percent of breast cancer cells and shrinks lung tumors
- Ginger over chemo: This powerful root can eliminate 10,000x the number of cancer cells
- HPV and Hepatitis B vaccines do not prevent cervical cancer and liver disease
- Four natural remedies for a quick and easy gut detox
- Newly released JFK files reveal Pentagon's role in creating Lyme disease and covid in the same lab
- EPA advisor admits the agency is funneling billions to climate groups ahead of Trump’s return to White House
- Eleven days before Iran bombed Tel Aviv, my microscope revealed haunting images of EXACTLY what would happen
- Morphic resonance “remote viewing” reveals iconic Middle East images of stealth bombers, a falcon and a one-horned ram
- Mike Adams releases country western hit single: Goin’ Back in Time is Comin’ Home
- DECENTRALIZED SPIRITUALITY and the true teachings of Christ: Overcoming the censorship, threats and lies of organized religion to truly know God and the Universal Christ
- HEALTH SECRETS: How to Instantly Block MSG Toxicity Using Natural Substances (and the secret of Methylene Blue)
- The Health Ranger releases “Vaccine Zombie” song and music video, using AI-animated zombies for the music video
- BOMBSHELL: Internal Pfizer documents exposed and reveal at least 16 PERCENT of their mRNA vaccine "adverse events" are REPRODUCTIVE DISORDERS
- Global leaders unite to clamp down on “misinformation” with UN-backed Cascais Declaration
- I Want My Bailout Money – new song released by Mike Adams
- BOMBSHELL: DNA testing kits are a SCAM to develop ethnic-specific bioweapons
- Amazing microscopy photos reveal how freezing crystals attempt to mimic electronic structures they are touching
- RFK Jr. clears key hurdle: Sen. Susan Collins backs controversial HHS nominee, signaling a new era for health policy
- BOMBSHELL: Covid-19 mRNA nanoparticles EMIT LIGHT SIGNALS that communicate MAC addresses used for self-assembly inside the blood vessels
- The Coming Gold Revaluation: Strategic Financial Realignment in an Era of Dollar Collapse
- The AI Data Center Wars Have Begun… Farms, Water and Electricity is Stripped from Humans to Power the Machines
- Urgent Wake-Up Call: The Coming AI Robot Wars and the Great Human Unity
The company made the announcement as the ongoing Ebola epidemic continues to grab headlines around the world. To date, more than 7,470 people have become infected, nearly all of whom in West Africa, and at least 3,439 people have died. Yet these number are widely regarded as severe underestimates. In addition, the number of people infected with the disease is doubling every 20 to 30 days.
Ebola is a viral disease spread by close contact with bodily fluids such as blood, vomit or diarrhea. Between 60 and 90 percent of infections end with death.
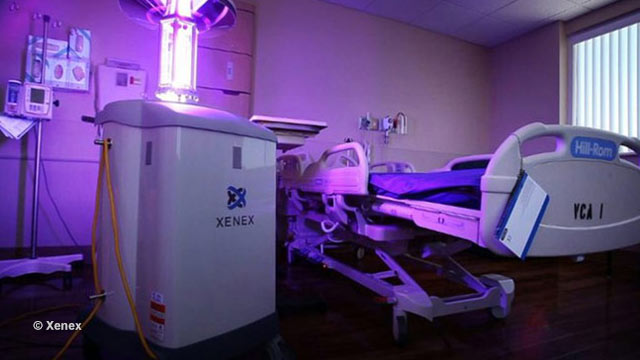
Robot sterilizes rooms remotely
According to Xenex, Little Moe destroys the DNA of viruses using a variety of ultraviolet radiation known as UV-C. Along with the more familiar UV-A and UV-B rays which promote vitamin D synthesis and can lead to sunburn in excessive amounts, UV-C rays are also emitted by the sun. But because the Earth's ozone layer prevents UV-C rays from reaching the surface, organisms have not evolved resistance to them as they have to UV-A and UV-B.Little Moe is an automated robot with a 62-inch, extendable neck. The neck contains a special bulb that fires 1.5 UV-C pulses per second in all directions, delinking and fusing the DNA of microorganisms. Because UV-C rays can damage the human eye, the robot is designed to be placed in an empty room and operated remotely. According to Xenex, the UV rays cannot pass through walls, windows or hospital safety glass.
Little Moe is just one of a myriad of measures now being suggested to help stem the uncontrolled spread of Ebola. Most such efforts, however, have focused on pharmaceutical drugs rather than medical devices.
Drug companies are scrambling to develop a vaccine for the disease and have turned to analyzing the blood of people who have recovered from Ebola infections. Indeed, blood transfusions from survivors appear to improve the recovery chances of current Ebola patients, suggesting that perhaps antibodies against the disease can be transferred from one person to another. British Ebola survivor William Pooley has recently traveled to the United States to donate his blood for vaccine research.
Drugs also being tested
A number of different companies are also testing out experimental drugs to treat people who have already contracted Ebola. The most famous of these, ZMapp, has already been used experimentally to treat seven people, five of whom later recovered. This use liquidated all existing supplies of the drug, however, and the company has announced that it will take months to make more. Yet the drug has also shown promise in one animal study, published in the journal Nature on August 29: Of 18 rhesus monkeys infected with the virus and given ZMapp within five days, 100 percent recovered.Dallas Ebola patient Thomas Duncan is being treated with another experimental drug, named brincidofovir. Unlike ZMapp, which consists of a cocktail of antibodies, brincidofovir is an anti-retroviral drug, much like HIV medications.
Other experimental Ebola drugs include the flu drug favipiravir (T-705) and the drug BCX4430. Canadian company Tekmira was testing another drug, but those trials have been halted due to safety concerns.
Doctors emphasize that no drug has yet been proven effective against Ebola. In contrast, proper supportive care such as hydration, saline solution and oxygen treatment has been proven to improve survival rates.
Learn all these details and more at the FREE online Pandemic Preparedness course at www.BioDefense.com
Sources:
http://indiatoday.intoday.in
http://www.independent.co.uk
http://www.nbcnews.com
http://www.naturalnews.com
http://science.naturalnews.com
Ebola at FETCH.news
Get independent news alerts on natural cures, food lab tests, cannabis medicine, science, robotics, drones, privacy and more.
More news on Ebola
Take Action: Support Natural News by linking to this article from your website
Permalink to this article:
Embed article link: (copy HTML code below):
Reprinting this article:
Non-commercial use OK, cite NaturalNews.com with clickable link.
Follow Natural News on Facebook, Twitter, Google Plus, and Pinterest
Science News & Studies
Medicine News and Information
Food News & Studies
Health News & Studies
Herbs News & Information
Pollution News & Studies
Cancer News & Studies
Climate News & Studies
Survival News & Information
Gear News & Information
News covering technology, stocks, hackers, and more


"Big Tech and mainstream media are constantly trying to silence the independent voices that dare to bring you the truth about toxic food ingredients, dangerous medications and the failed, fraudulent science of the profit-driven medical establishment.
Email is one of the best ways to make sure you stay informed, without the censorship of the tech giants (Google, Apple, Facebook, Twitter, YouTube, etc.). Stay informed and you'll even likely learn information that may help save your own life."
–The Health Ranger, Mike Adams























